

Part of a special issue, Ontologies of Living Beings, guest-edited by A. Results of this examination include a (partial) characterization of stem cells’ developmental versatility, and the context-dependence of developmental processes involving stem cells. The concept of ‘enkapsis’ accommodates the cell-organism relation within the lineage view this hierarchical notion is further explicated by considering the methods and results of stem cell experiments.
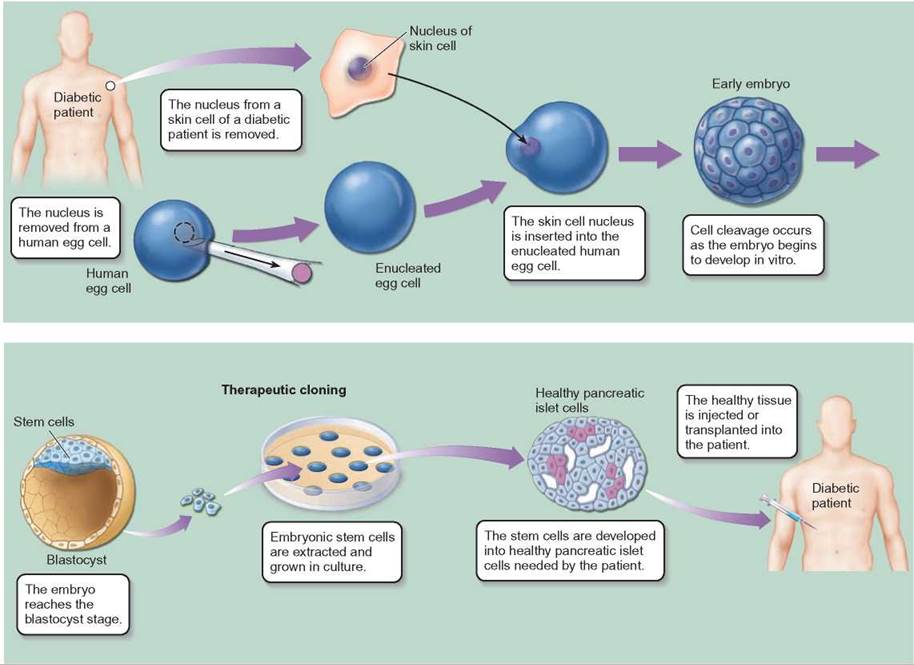
On the lineage view, a stem cell is the starting point of a cell lineage with a specific organismal source, time-interval of existence, and ‘tree topology’ of branch-points linking the stem to developmental termini. This account is grounded on experimental practices of stem cell research, with emphasis on new techniques for generating biological organization in vitro. This paper aims to fill the gap, proposing the lineage view of stem cells as an ontological framework for conceptualizing organismal development. However, recent accounts of these concepts do not engage developmental biology. The process of development is thus prima facie central for ideas about biological individuality and organismality. Biological development is a process, undergone by living things, which begins with a single cell and (in an important class of cases) ends with formation of a multicellular organism. Ontologies of living things are increasingly grounded on the concepts and practices of current life science. Ultimately the development of more pathophysiologically relevant disease model systems enables us to efficiently develop and assess new therapeutic targets and potential treatments.Received 2 September 2016 Accepted 20 February 2017 Abstract This approach enables us to track how healthy cells change in disease, which in turn enables us to better define disease model systems. The first step in this model development program is defining conditions that permit the generation of specific cell types (for example, A9 or A10 midbrain dopaminergic neurons), the second step is defining conditions that reflect the environment associated with disease (if possible). My research is largely focussed on the development of models of neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases.
The Stem Cell Group at MIPS has generated a number of embryonic stem cell reporter lines enabling the identification of particular neurons in culture. Much of the focus of stem cell biology is directed at the specification of particular cellular phenotypes (neurons, cardiomyocytes, blood, etc.) for use in cell replacement therapies, drug screening and disease modelling. Stem cells can self-renew indefinitely and, being pluripotent, they can develop into any cell type present in the adult. Note the microdomain signalling associated with the extensive endoplasmic reticulum. A calcium fluorophore-loaded astrocyte responding to PGE2.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
