
Needles or numbness with or without associated weakness e.g. Altered Sensation: the pain may progress to pins and.Pain: in the lower back which may spread down through the buttock,īack of the leg and sometimes the foot.The most common symptoms of nerve pain in the foot from a herniated disc are: When you squeeze a donut, the jam leaks out the back, sticking to whatever it touches. Think of it like a jam donut, where the donut represents the disc, and the jam represents the nucleus. If discs get squashed too much, some of the material from the middle of the disc (the nucleus) gets pushed out of the back of the disc, irritating and/or squashing the nerve root. Herniated Disc aka Slipped Discīetween most of the vertebrae in our back there are discs that provide cushioning and allow pain-free, flexible movement. The two most common problems in the lower back that can damage the sciatic nerve and thus cause nerve pain in foot are: 1. If the sciatic nerve is squashed anywhere along its path, it interrupts the signals travelling up and down the nerves to the spinal cord resulting in pain, weakness, tingling or numbness anywhere in the leg and down in to the foot.

The sciatic nerve travels down through the buttock and the back of the leg, branching out as it spreads further down through the leg and into the foot. At the base of the spine, five nerves (L4, 5, S1, 2 &3) exit the spine and join together to form the sciatic nerve, the largest nerve in the body. Nerve pain in the foot often comes from a problem in the back, rather than in the foot itself. Neuropathic pain is often worse at night due to inflammation and often leads to foot pain in the morning. causing nerve pain in foot or tingling/pins and needles. causing numbness or weakness, or fire erratically, sending excessive or incorrect signals e.g. They may stop sending messages altogether e.g. Autonomic Nerves: control things like bladder and bowel function, heart rate and digestionĭamage to the nerves causes them to behave abnormally.Motor Nerves: control how the muscles work telling them when, how long and how strongly they should contract and relax.Sensory Nerves: receive information on different sensations such as hot/cold, sharp/dull, light/heavy pressure.There are three types of nerves in our bodies: The peripheral nerves take messages to and from the brain and spinal cord which interpret the messages and send a responding signal back down to the starting point. Our nervous system is made up of two systems, the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system (nerves).
DIAGRAM OF NERVE ENDINGS IN FEET HOW TO
Here, we will look at how nerves work, the most common causes of foot and leg nerve pain, how they present and how to know when nerve pain in foot is a medical emergency. In this case symptoms tend to be localized to the foot and possibly lower leg.
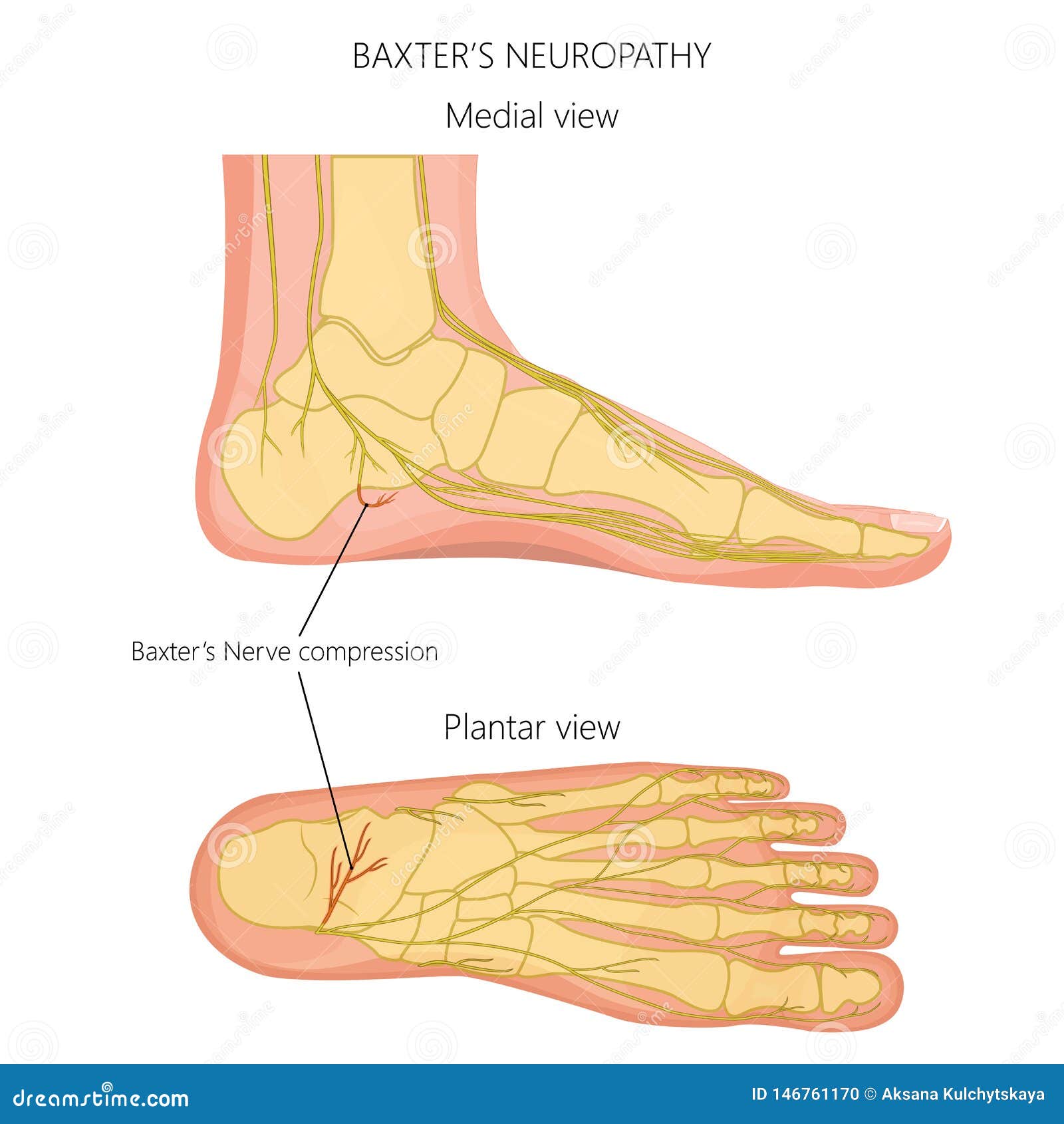
The Spine: Damage to the lower back is a common cause of nerve pain in the foot.Nerve pain in foot can stem from two places: Nerves are responsible for carrying messages telling muscles how and when to work, providing information on different sensations such as hot and cold and controlling various bodily functions.ĭamage anywhere along the course of a nerve affects its ability to carry these messages and can cause nerve pain in foot, also be known as a foot neuropathy or neuropathic pain. This is usually either from an injury to the back, leg or foot, an underlying medical condition or a side effect of medication. Nerve pain in the foot is typically caused by damage to the nerve somewhere along its path from the spine down to the foot. Symptoms may be confined to the foot however they often affect the leg too. There may be burning foot pain, tinging, numbness or weakness. Nerve pain in the foot is a common problem.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
